Fix Invalid Traffic Sources That Google May Penalize For Ad Serving

As a publisher, invalid traffic is a major threat to your site’s ability to monetize with a number of models. Fixing the source of invalid traffic is essential to maintaining good standing with Google Ad products, like AdSense and Adx, and major affiliate networks, like Amazon. Websites need to find and fix invalid traffic sources or they could risk Google, or other partners, suspending their ability to monetize with their networks or products.
Invalid traffic is a growing threat to publishers monetizing their site with display ads because Google doesn’t provide a warning prior to disabling a Google Publisher Account due to invalid traffic. What’s more, is that due to Google’s need to protect their proprietary detection system for invalid traffic that they can’t give you any specific information on what caused your account to be disabled.
A frustrating conundrum for any sites using AdSense or Google Adx as a primary source of display ad revenue on their site (note: this is the majority of publishers). Google can tell you that they have found invalid traffic but can’t tell you what it is or where it’s coming from.
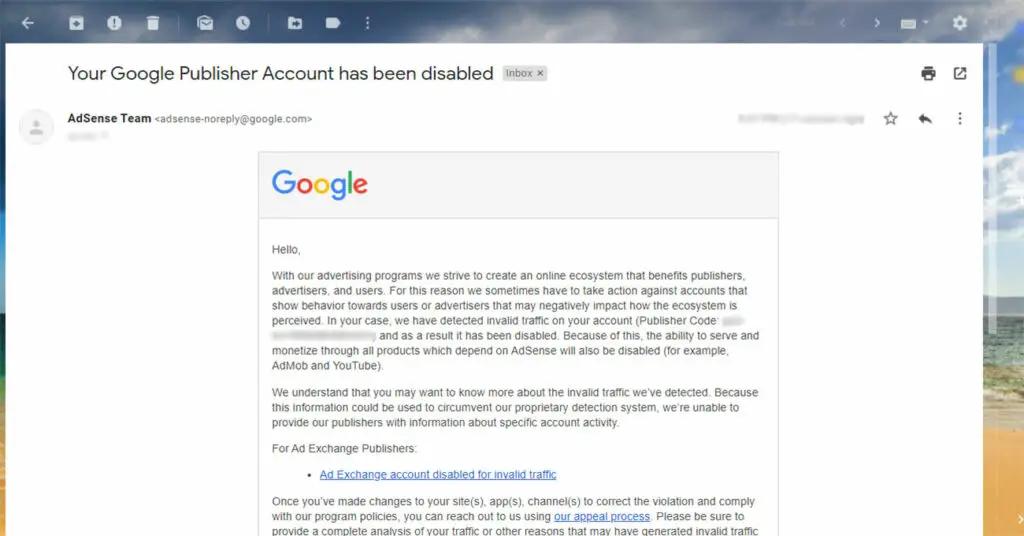
_This is an example of an email from the AdSense team that had their account disabled because of invalid traffic._
The best way to avoid Google penalizing you for invalid traffic is to **prevent invalid traffic from occurring**. Easier said than done.
Today, I’m going to show you how to prevent a few forms of invalid traffic that are within your immediate control. There is also a video below.
How Google detects invalid traffic sources
Since websites that are being flagged for invalid traffic have AdSense / Google ad tags on the page, Google can see the user agent and also read any data that JavaScript could request when embedded in the page.
Think of it this way, at minimum, Google can detect anything Google Analytics detects when their ad tags are on the page.
Recently, Google Analytics shared that it is no longer is recording bot traffic or invalid traffic in GA by default. There’s a setting in Google Analytics admin that allows you to toggle that on or off, which I will cover in the next section. What Google Analytics filters out when that is toggled could be somewhat representative of what they are detecting using other products too.
Outside of this information, there’s not much else that can be shared about Google’s detection methods. Most others in the industry are forced to take a very reactive approach to understand what caused invalid traffic issues and are tasked with identifying [patterns that could be specific to different types of invalid traffic](https://www.google.com/ads/adtrafficquality/tag-taxonomy.html).
Is invalid traffic bot traffic?
Invalid traffic is not _always_ bot traffic. Because there are more types of invalid traffic than just bot traffic.
Google [defines invalid traffic](https://support.google.com/adsense/answer/16737?hl=en) as:
- Clicks or impressions generated by publishers clicking their own live ads
- Repeated ad clicks or impressions generated by one or more users
- Publishers encouraging clicks on their ads (examples may include: any language encouraging users to click on ads, ad implementations that may cause a high volume of accidental clicks, etc.)
- Automated clicking tools or traffic sources, robots, or other deceptive software.
One of the easiest ways to help prevent invalid traffic is to **toggle on the “bot filtering” setting in Google Analytics Admin settings.** This setting will “exclude all hits from known bots and spiders.”
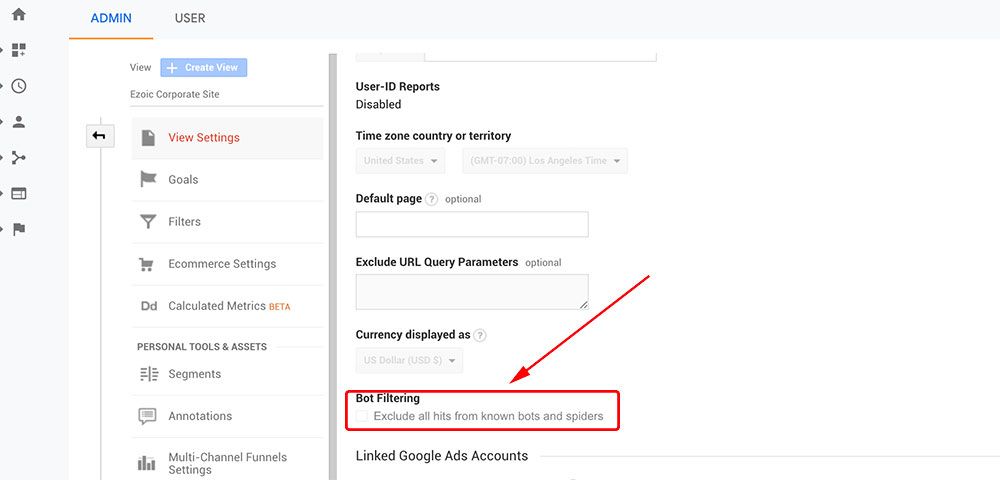
This will simple filter the bots, it doesn’t eliminate them; however, seeing reports with and without the filtering could provide some evidence of where the bots traffic may be coming form.
Adding to the growing issue is that bots are more intelligent than ever before. [Now, you can even rent a full bot-net for less than $20 USD](https://www.imperva.com/learn/application-security/booters-stressers-ddosers/). Bad actors are seemingly always one step ahead.
What is the source of invalid traffic?
If you have been notified by Google that your website is being hit with invalid traffic, you are one of two people looking for this article:
1. You’re doing nothing wrong at all, and the invalid traffic is a mystery.
2. You’re not being honest with yourself and the invalid traffic is a byproduct of something intentional.
Almost everybody is going to say they’re in this first category. If you’re in the second category, **this article isn’t for you**.
Additionally, if you were doing this intentionally, all you would have to do is remove the invalid traffic and continue doing the scam. That’s why Google Analytics doesn’t give you exactly _what traffic_ is invalid.
So what do you do when you’re not doing this intentionally and you don’t know what traffic is invalid? You’re in the dark and trying to find a ghost. While there are many causes of invalid traffic, I’m going to share with you the three that I’ve seen recently cause unintentional invalid traffic for publishers.
3 major causes of unintentional invalid traffic
1\. Buying expired domains or redirecting old sites to a new **one**
Buying expired domains has the potential to send unwanted, spammy redirected traffic your way. This is a common SEO practice that many don’t often connect to unwanted, invalid traffic.
The benefits of using expired domains to redirect to your own site or to build a new one:
- The expired domain may have good authority
- Good backlinks still pointing to that domain
- It’s a domain name in a similar niche as your own site
- Have a .edu / .org address which has [higher levels of authoritativeness](/?p=10902)
When publishers do this, the thought is the backlinks and domain information will be passed onto the new site once a redirect is set up. Or, if you use the expired domain to [build a website](/?p=49886), the established authority will help boost authority and rankings.
The problem is when you purchase these domains, **you don’t know is who is sending traffic to these domains and why**. Additionally, it’s difficult to know which websites might be pinging that expired site regularly simply because they knew it was expired.
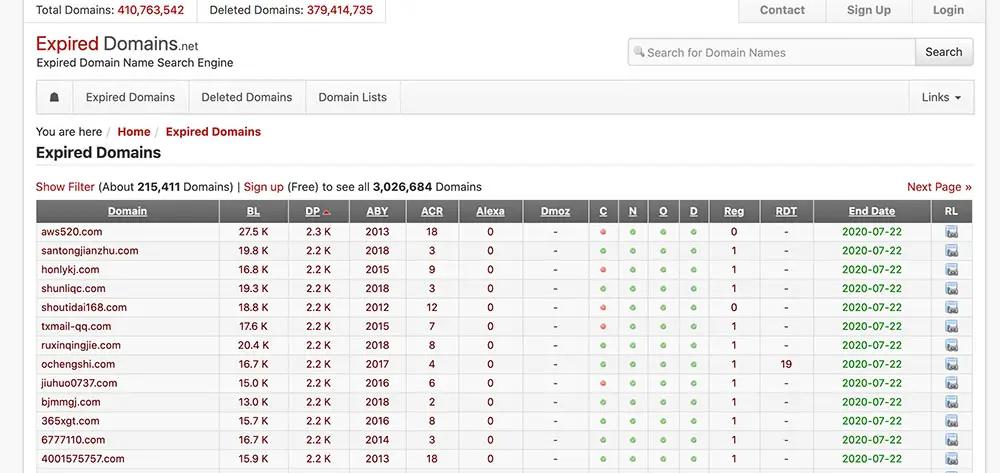
What forwarding traffic from these expired domains to your new sites can lead to:
- Bots and crawlers coming to your website.
- Visitors that bounce immediately (which you don’t want) when the old website gets forwarded they realize, “This isn’t the site I was looking for.”
- Invalid traffic warnings from Google
How to prevent:
To solve this issue, you have to go back and see what expired domains are forwarding to your site. Additionally, it’s worth looking at where traffic is coming from for those sites.
To do this, you need to look at your server log files. If there is Google Analytics for those particular URLs, you should look at it. You should also look at **how many times a redirect is hit**, whether at your host or if you have WordPress set up you can actually see what redirects are being hit. If you’re redirecting some of these sites, you might be able to see where some of their (the expired domain’s) traffic is coming from.
> **Remember:** The whole point was just to get the information from the links passed to your new site, **not necessarily to the traffic**.
This can be a difficult one to solve especially if it’s a strategy you’ve already invested in. A lot of people don’t want to admit this happens, because it’s touted as a great strategy with no downsides. But this is one of the downsides that SEO people forget about or tend to ignore.
You may be able to setup domain-forwarding to filter out bots through your CDN or host if you’d like to put effort toward keeping the backlinks in place while still protecting against bot traffic. [Cloudflare](https://www.cloudflare.com/) has some good options for this.
2\. Being an easy hacking target
Bots are becoming an increasingly common part of all of web traffic. While there are good bots, like Google’s web crawler (Googlebot), there are also bad bots.
Bad bots range from scrapers that duplicate or steal content, emails, etc. to click bots that click display ads. There are even bots that try to hack into websites’ CMS. Imperva’s 2019 Bad Bot Report found that bad bots accounted for [24.1% of all web traffic](https://www.imperva.com/resources/resource-library/reports/2020-Bad-Bot-Report/).
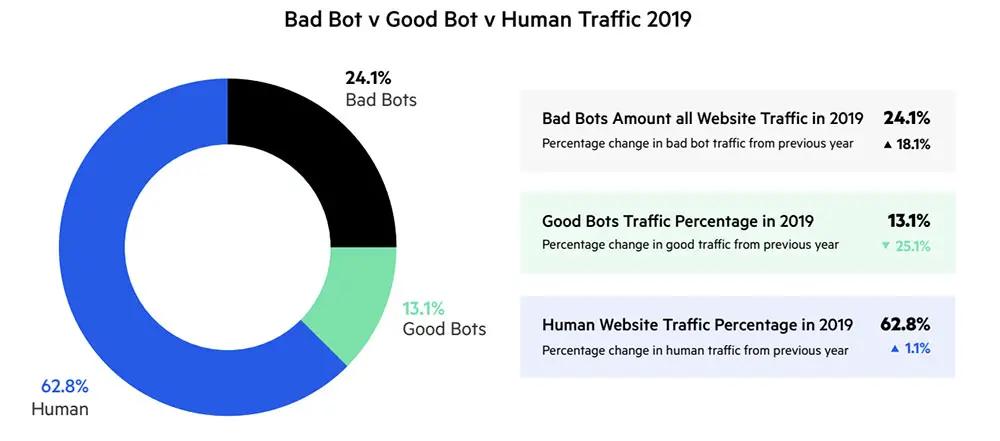
The biggest rise of bad bot behavior is credential hacking and credential stuffing. Imperva claims to have mitigated an attack that lasted 60 hours and included 44 million login attempts. These types of high-volume DDoS attacks can put a major strain on a network, or take it down completely.
How to prevent:
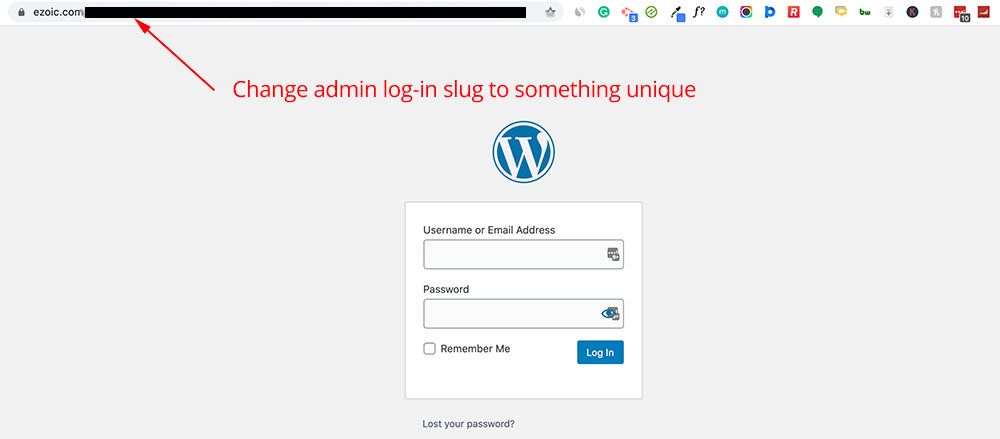
An easy way to prevent bad bots from hacking into your CMS is to set your admin login URL to something different than the default.
> **For example:**
>
> **Instead of:** www.website.com/myadminportal
>
> **Change to:** www.website.com/myadminportal\_12
If your website is the default admin login URL, bad bots will hit that page. This is because all websites of a certain CMS share the same default admin login URL. WordPress sites are www.examplesite.com/wp-admin and Joomla sites are commonly www.examplesite.com/administrator.
Lastly, Two ways to further safeguard your website from bad bots is to guard against enumerating user attacks. If you use WordPress, this [enumerated user plugin](https://wordpress.org/plugins/stop-user-enumeration/) has the highest ratings.
User Enumeration is a type of attack where bad bots can probe your website to discover your login name (or other users’ logins). This is often a pre-cursor to brute-force password attacks. Plugins like these help block attacks and even allows you to log IPs launching these attacks to block further attacks in the future.
With these changes in places, you should be able to avoid invalid traffic by blocking bad bots from attacking your website.
**3\. Sharing content and “link-building”**
Sharing content and [“link-building”](/?p=13983) are common practices espoused by SEO folks online. Some publishers share links to their site in comment sections, online listings, and forums. These tactics are just whitehat SEO techniques, right? Not so fast.
These are places where it’s highly possible that **web crawlers may try to crawl those pages.** This then puts your website in a position ripe for having crawlers hitting your site’s pages with a lot of frequency. If the crawler is unsophisticated or the link is on a page that is hit by bots often, this behavior can trickle down **to more invalid traffic being funneled to your site.**
These types of tactics are what I would describe as very unnatural. Meaning, you’re trying to post links in comment sections, just trying to make your content ‘available’ to those people. It’s basically unpaid marketing, and it’s spammy. Google will catch on.
The more often you link your site in online listings where it may or may not make sense, the more likely web crawlers are likely going to hit it
How to prevent:
The only way to prevent invalid traffic from sharing content or link-building is simply **not to do it in places that are unnatural.** Don’t spam your links in comment sections of websites, aggressively in online listings or forums (without context), or spam people’s emails with links.
Wrapping up how to prevent invalid traffic warnings Google may penalize
These are the 3 common practices most people are unaware of that can drive invalid traffic to your website.
1. Buying expired domains or redirecting them to new websites
2. Being an easy hacking target
3. Sharing content or link-building
If all else fails, talk to your host. Ask them if there’s been any activity that’s been reported to them. You pay them for hosting, so ask them if they can help you because your site is experiencing unusual traffic from bots that are potentially critically damaging your online business.
Have any questions about how to prevent invalid traffic deactivation from Google? Let me know in the comments. I can promise that I won’t have all the answers but perhaps myself or others can share something helpful.